Doxycycline hyclate
Product Description
Doxycycline Hyclate, is a syntheic oxytetracycline broad-spectrum antibiotic, primarily targeting bacteria responsible for respiratory infections, including Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenza. Additionally, it can be used to treat variety of infections such as Lyme disease, Rickettsia, and some spirochetes, and has antigenic and insect repellent functions. Doxycycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Doxycycline Hyclate is also an inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), including MMP-8 (neutrophil collagenase; IC50: 30 μM) and MMP-1 (interstitial collagenase; IC50: 300 µM). Doxycycline Hyclate has been observed to significantly decrease the levels and activity of metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in corneal erosion studies. Doxycycline Hyclate blocks collagen activity and increases smooth muscle cell adhesion, and changes the reorganization of fibrillar collagen matrices and cell migration in smooth muscle studies. Doxycycline hydrochloride is also commonly used in tet-on (rtTA dependent) and tet-off (tTA dependent) systems to regulate gene expression, both in vivo and in vitro.
Product Properties
|
Synonyms |
Doxycycline hydrochloride hemiethanolate hemihydrate; WC2031 |
|
CAS# |
24390-14-5 |
|
Formula |
C22H24N2O8·HCl·0.5H2O·0.5C2H6O |
|
Molecular Weight |
512.94 |
|
Appearance |
Light yellow powder |
|
Potency (Anhydrous) |
800 - 920 μg/mg |
|
Grade |
USP |
|
Solubility |
Soluble in water (≥ 100 mg/mL), DMSO (≥ 100 mg/mL) and methanol. Insoluble in chloroform. |
|
Structure |
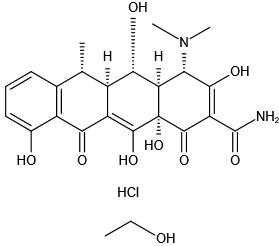 |
Shipping and Storage
The product is shipped with ice pack and can be stored at 2-8℃ for 2 years. The aqueous solution can only be stored stably at 4 ℃ for 5 days, and can be stored at for a longer term at -20 ℃.
Cautions
1. For your safety and health, please wear lab coats and disposable gloves for operation.
2. For research use only.
[1] Zhu G, Xie J, Kong W, et al. Phase Separation of Disease-Associated SHP2 Mutants Underlies MAPK Hyperactivation. Cell. 2020;183(2):490-502.e18. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.002(IF:38.637)
[2] Gao XK, Rao XS, Cong XX, et al. Phase separation of insulin receptor substrate 1 drives the formation of insulin/IGF-1 signalosomes. Cell Discov. 2022;8(1):60. Published 2022 Jun 28. doi:10.1038/s41421-022-00426-x(IF:10.849)
[3] Jiao X, Wang B, Yang L, et al. FMNL2 suppresses cell migration and invasion of breast cancer: a reduction of cytoplasmic p27 via RhoA/LIMK/Cofilin pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):155. Published 2022 Apr 4. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-00964-z(IF:5.241)
[4] Xu B, Zhang C, Jiang A, et al. Histone methyltransferase Dot1L recruits O-GlcNAc transferase to target chromatin sites to regulate histone O-GlcNAcylation. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(7):102115. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102115(IF:5.157)
[5] Gong Z, Liu X, Wu J, et al. pH-triggered morphological change in a self-assembling amphiphilic peptide used as an antitumor drug carrier. Nanotechnology. 2020;31(16):165601. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/ab667c(IF:3.551)
Catalog No.:*
Name*
phone Number:*
Lot:*
Email*
Country:*
Company/Institute:*
Related articles

